Product Description
SC Transmission FCL Flange Flexible Coupling
Product Description
CHARACTERISTICS
FCL Coupling Flange Coupling has simple construction that makes it:
Easy to assemble and disassemble, easy parts replacement.
It is able to transmits power smoothly even under vibration and shock due to its ability to absorb shock and load vibration.
It is also able to transmit power under parallel and angular misalignment, and end-floating.
Smooth running.
Permit reverse revolution.
Full range available from Size 90 to 630
Applications
SC Transmission flange flexible coupling has a wide range of applications: pump, blower, compressor, conveyor, crane & hoist, cement mixer, tractor, rolling mill, metal processing machine, spinning and weaving machinery etc.
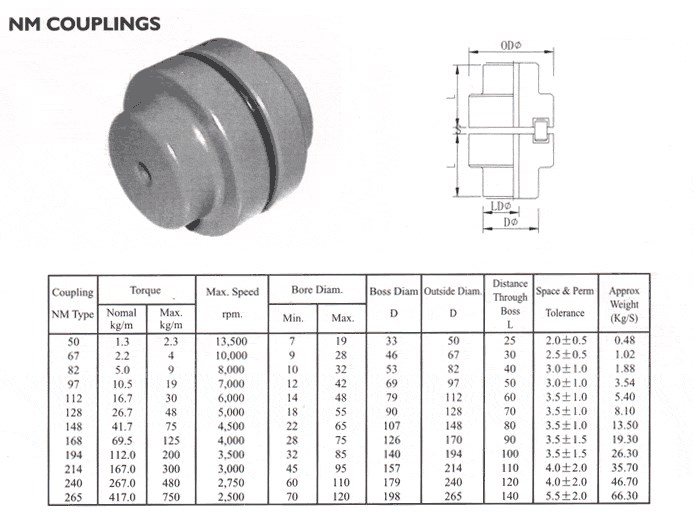
Product Parameters
| SIZE | D | D1 | d1 | L | C | n-M | kg | |||
| r/min | ||||||||||
| N.m | ||||||||||
| FCL90 | 4 | 4000 | 90 | 35.5 | 11 | 28 | 3 | 4-M8 | 1.7 | |
| FCL100 | 10 | 4000 | 100 | 40 | 11 | 35.5 | 3 | 4-M10 | 2.3 | |
| FCL112 | 16 | 4000 | 112 | 45 | 13 | 40 | 3 | 4-M10 | 2.8 | |
| FCL125 | 25 | 4000 | 125 | 65 | 50 | 13 | 45 | 3 | 4-M12 | 4 |
| FCL140 | 50 | 4000 | 140 | 71 | 63 | 13 | 50 | 3 | 6-M12 | 5.4 |
| FCL160 | 110 | 4000 | 160 | 80 | 15 | 56 | 3 | 8-M12 | 8 | |
| FCL180 | 157 | 3500 | 180 | 90 | 15 | 63 | 3 | 8-M12 | 10.5 | |
| FCL200 | 245 | 3200 | 200 | 100 | 21 | 71 | 4 | 8-M20 | 16.2 | |
| FCL224 | 392 | 2850 | 224 | 112 | 21 | 80 | 4 | 8-M20 | 21.3 | |
| FCL250 | 618 | 2550 | 250 | 125 | 25 | 90 | 4 | 8-M24 | 31.6 | |
| FCL280 | 980 | 2300 | 280 | 140 | 34 | 100 | 4 | 8-M24 | 44 | |
| FCL315 | 1568 | 2050 | 315 | 160 | 41 | 112 | 4 | 10-M24 | 57.7 | |
| FCL355 | 2450 | 1800 | 355 | 180 | 60 | 125 | 5 | 8-M30 | 89.5 | |
| FCL400 | 3920 | 1600 | 400 | 200 | 60 | 125 | 5 | 10-M30 | 113 | |
| FCL450 | 6174 | 1400 | 450 | 224 | 65 | 140 | 5 | 12-M30 | 145 | |
| FCL560 | 9800 | 1150 | 560 | 250 | 85 | 160 | 5 | 14-M30 | 229 | |
| FCL630 | 15680 | 1000 | 630 | 280 | 95 | 180 | 5 | 18-M30 | 296 | |
Company Profile
FAQ
Shipping
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 11-95 |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Material: | Cast Iron |
| Type: | FCL Coupling |
| Transport Package: | Plywood Case |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What industries commonly use flexible couplings for power transmission?
Flexible couplings are widely used in various industries for power transmission and motion control applications. Their ability to accommodate misalignment, dampen vibrations, and protect equipment from shock loads makes them valuable components in many industrial processes. Here are some of the industries that commonly utilize flexible couplings:
- Manufacturing: Flexible couplings are extensively used in manufacturing industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods production. They play a critical role in transmitting power between motors and various machinery, including conveyor systems, robots, and assembly lines.
- Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas industry, flexible couplings are used in pumps, compressors, turbines, and generators. They help transfer power in offshore platforms, refineries, pipelines, and drilling operations while compensating for the dynamic nature of these applications.
- Power Generation: Power plants, both conventional and renewable, rely on flexible couplings to transmit power from turbines and generators to electrical generators. They are used in coal-fired, natural gas, nuclear, hydroelectric, and wind power plants.
- Mining: In mining operations, flexible couplings are employed in various equipment, including conveyor systems, crushers, and large industrial pumps. They are designed to withstand the heavy loads and harsh conditions commonly found in mining environments.
- Marine: Flexible couplings are essential in marine propulsion systems, connecting engines to propellers or water jets. They also find use in shipboard machinery, auxiliary systems, and offshore applications.
- Pulp and Paper: The pulp and paper industry relies on flexible couplings in machinery used for wood processing, pulp production, papermaking, and printing processes.
- Chemical and Petrochemical: In chemical plants and petrochemical refineries, flexible couplings are utilized in pumps, mixers, agitators, and other rotating equipment to ensure efficient power transmission and protect sensitive machinery.
- Construction: The construction industry employs flexible couplings in various equipment, such as concrete pumps, cranes, excavators, and drilling machines.
- Water and Wastewater: Flexible couplings are used in water treatment plants, wastewater facilities, and irrigation systems to transfer power between motors and pumps.
- Agriculture: In agricultural machinery, flexible couplings are utilized in tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems, enabling efficient power transmission and operation.
The versatility and adaptability of flexible couplings make them indispensable components in a wide range of industries, contributing to increased equipment reliability, reduced downtime, and improved overall system performance.

What are the factors to consider when choosing a flexible coupling for a specific system?
Choosing the right flexible coupling for a specific system requires careful consideration of several factors. The following are the key factors that should be taken into account:
- 1. Misalignment Requirements: Assess the type and magnitude of misalignment expected in the system. Different couplings are designed to handle specific types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, or axial misalignment. Choose a coupling that can accommodate the expected misalignment to prevent premature wear and failure.
- 2. Torque Capacity: Determine the required torque capacity of the coupling to ensure it can transmit the necessary power between the shafts. Consider both the continuous and peak torque loads that the system may experience.
- 3. Operating Speed: Take into account the rotational speed of the system. High-speed applications may require couplings that can handle the additional centrifugal forces and balance requirements.
- 4. Temperature Range: Consider the operating temperature range of the system. Select a coupling material that can withstand the temperatures encountered without losing its mechanical properties.
- 5. Environment and Conditions: Evaluate the environmental conditions where the coupling will be used, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, dust, or corrosive substances. Choose a coupling material that is compatible with the operating environment.
- 6. Space Constraints: Assess the available space for the coupling installation. Some couplings have compact designs suitable for applications with limited space.
- 7. Installation and Maintenance: Consider the ease of installation and maintenance. Some couplings may require special tools or disassembly for maintenance, while others offer quick and simple installation.
- 8. Torsional Stiffness: Evaluate the torsional stiffness of the coupling. A balance between flexibility and stiffness is essential to prevent excessive torsional vibrations while accommodating misalignment.
- 9. Shock and Vibration Damping: For applications with high shock loads or vibration, select a coupling with excellent damping characteristics to protect the system from excessive forces.
- 10. Cost and Budget: Compare the cost of the coupling with the overall budget for the system. Consider the long-term cost implications, including maintenance and replacement expenses.
Ultimately, the choice of a flexible coupling should align with the specific requirements and operating conditions of the system. Consulting with coupling manufacturers or engineering experts can provide valuable insights to ensure the optimal selection of a coupling that enhances system performance, reliability, and efficiency.

Can flexible couplings handle misalignment between shafts?
Yes, flexible couplings are specifically designed to handle misalignment between shafts in rotating machinery and mechanical systems. Misalignment can occur due to various factors, including installation errors, thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, or shaft deflection during operation.
Flexible couplings offer the ability to compensate for different types of misalignment, including:
- Angular Misalignment: When the shafts are not collinear and have an angular offset, flexible couplings can accommodate this misalignment by flexing or twisting, allowing the two shafts to remain connected while transmitting torque smoothly.
- Parallel Misalignment: Parallel misalignment occurs when the two shafts are not perfectly aligned along their axes. Flexible couplings can adjust to this misalignment, ensuring that the shafts remain connected and capable of transmitting power efficiently.
- Axial Misalignment: Axial misalignment, also known as end float or axial displacement, refers to the relative axial movement of the two shafts. Some flexible coupling designs can accommodate axial misalignment, allowing for slight axial movements without disengaging the coupling.
The ability of flexible couplings to handle misalignment is essential in preventing premature wear and failure of the connected equipment. By compensating for misalignment, flexible couplings reduce the stress on the shafts, bearings, and seals, extending the service life of these components and improving overall system reliability.
It is crucial to select the appropriate type of flexible coupling based on the specific misalignment requirements of the application. Different coupling designs offer varying degrees of misalignment compensation, and the choice depends on factors such as the magnitude and type of misalignment, the torque requirements, and the operating environment.
In summary, flexible couplings play a vital role in handling misalignment between shafts, ensuring efficient power transmission and protecting mechanical systems from the adverse effects of misalignment. Their ability to accommodate misalignment makes them indispensable components in various industrial, automotive, aerospace, and marine applications.


editor by CX 2023-11-16